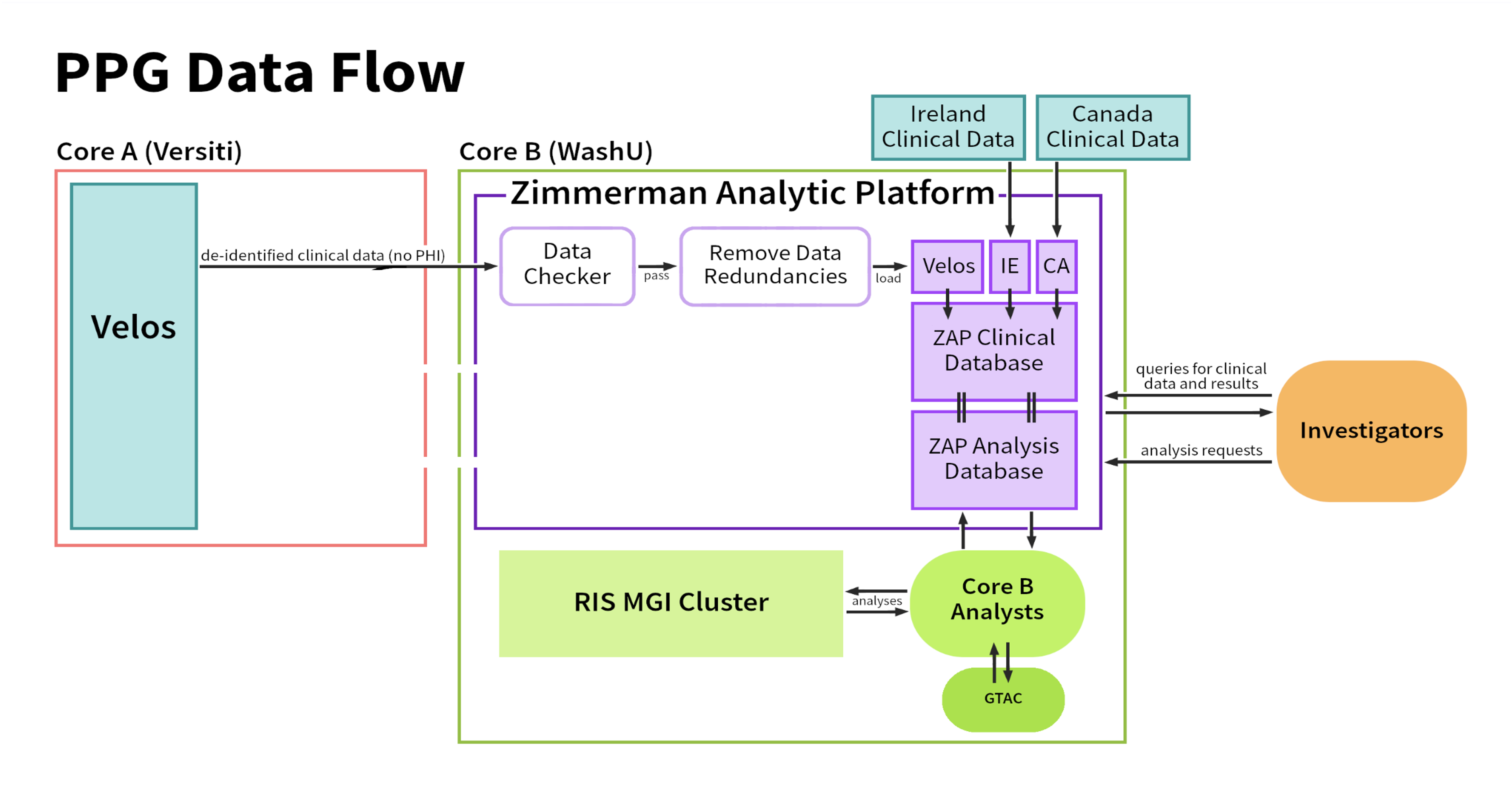
Zimmerman Analytic Platform (ZAP)

Zimmerman Program for Von Willebrand Disease
The foundation for this program project is to understand the biology of von Willebrand disease (VWD). It makes use of 2 large clinical VWD cohorts in the United States – one was a developed to characterize the historic diagnosis of VWD in the United States and the other to prospectively diagnose VWD patients that that are referred because of bleeding symptoms that require a diagnostic workup for VWD. Our overall hypothesis is that VWD can be caused by genetic mechanisms outside of the coding region but within or adjacent to the VWF locus (eg. 5’ upstream variants and intronic changes missed with aCGH), genes outside the VWF locus that affect synthesis or clearance, genes that affect carbohydrate modification of VWF, and epigenetic causes of altered s ynthesis or clearance. The combined VWD cohort (PPG + R01) of index cases includes 754 type 1, 3, or low VWF (LVWF) subjects (VWF:Ag <50 IU / Dl) and 172 type 2 VWD variants. Since there is an additional 2245 affected or unaffected family members, this offers us the clinical foundation to specifically characterize these comprehensive mechanisms causing VWD.